- Home
- Search
- Browse
- Hot topics
- Matrices
- About
- Help
- Contact
 Matrix cell
Matrix cell

Management/supervision; Safeguarding the community
Seminal and key studies on the role of management and supervision in relation to treatment in criminal justice settings and/or for the purpose of safeguarding the community. Just as for the practitioners, for managers the ‘tricky’ challenge is to extract therapeutic benefit out of a coercive, punishment-oriented context.
S Seminal studies
K Key studies
R Reviews
G Guidance
more Search for more studies
Links to other documents. Hover over for notes. Click to highlight passage referred to. Unfold extra text 
S
Watershed moment for the place of child protection in substance use policy and services ([UK] Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs, 2003). Though published in 2003, this report from the UK government’s drug policy advisers deserves the accolade of “seminal”. After its publication, no practitioner, manager or policy maker could justifiably claim ignorance of the need to prioritise the child while treating their parent(s) for substance use problems. It changed perspectives, lifting eyes from the direct treatment task to the family, and remains a key source for related guidance and research. Also listed below as guidance. For discussion click and scroll down to highlighted heading.
K
Daunting task of managing ‘wet’ day centres (2003). Describes the set-up and management challenges faced by UK centres offering street drinkers a place where they can start to reverse years of deterioration – without having to stop drinking. Related study below. For discussion click and scroll down to highlighted heading.
K
Management problems undermine hostel for drinkers (1999). In London’s East End a project to house rough sleepers unwilling to stop drinking curtailed local ‘nuisance’ from street drinking and begging, but was at first undermined by unsuitable premises, staffing, and management. Related study above. For discussion click and scroll down to highlighted heading.
K
Leadership affects adoption of evidence-based practices (2008; alternative free source at time of writing). Leadership qualities including knowledge and experience and commitment to a rehabilitation focus predicted good substance use treatment practice in US criminal justice services. For discussion click and scroll down to highlighted heading.
K
Motivational interviewing style clashes with criminal justice context (2001). Actual performance of US probation staff after motivational interviewing training contradicted promising written responses, and the officers were rated as less ‘genuine’ than before – possibly because the work context limited how far they could genuinely stay true to motivational principles. Same study described in this Findings essay. Related discussion in cell B5’s bite.
K
Offender–intervention matching principles really do help (2011). Training probation officers in the risk-need-responsivity model intended to match interventions to the offender reduced the recidivism of offenders on probation. For discussions click here and here and scroll down to highlighted headings.
R
Female offenders particularly need holistic treatment (2008). Argues that treatment for female offenders should take into account the high prevalence of post-traumatic stress and other mental and physical health problems, and the significance for them of relationships and of their roles as mothers. Concludes that women respond best to holistic, integrated programmes which incorporate empowerment and peer mentoring, and adopt a collaborative rather than authoritarian approach.
R
Substance use practitioners can build on their skills to address child protection (2007). After reviewing international research, UK-based experts on the family dimensions of substance use problems questioned the commonly reported perception of substance use treatment workers that child welfare is beyond their skills and professional comfort zones. For discussion click and scroll down to highlighted heading.
R
G
Managing services for drink-drivers (Health Canada, 2004). Selected on the basis of a research review and expert opinion, recommended education, treatment and rehabilitation approaches to alcohol/drug impaired driving, plus training and organisational requirements for implementation.
R
G
Specific recommendations on training for treatment in a criminal justice context (Australian Government, 2005). Uniquely focuses on training staff to treat substance use problems in a criminal justice context, formulating guidance on training and its management based on a review of research specific to this context and more generic literature and principles. For discussions click here and here and scroll down to highlighted headings.
R
G
Creating and maintaining ‘family sensitive’ treatment services ([Australian] National Centre for Education and Training on Addiction, 2010). Reviews generic and substance use-specific research as a basis for guidance on workforce development policies and practices to help ensure treatment services safeguard their clients’ children. For related discussion click and scroll down to highlighted heading.
G
Child protection is part of the business of substance use services ([UK] Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs, 2003). Results of an inquiry into children in the UK seriously affected by parental drug use. Says that though “Our main focus is … on problem drug use … many of the recommendations … will also be applicable to the children of problem drinkers”. Includes (starting p. 82) guidance on incorporating child protection measures into the work of drug and alcohol services. Update published in 2006. Also listed above as a seminal report. For discussion click and scroll down to highlighted heading.
G
Scottish guidance on protecting families and children advocates “whole family” recovery (Scottish Government, 2013). Guidance specific to substance use intended for all child and adult services, including drug and alcohol services. Sees treatment of the parent’s substance use as one element of a “whole family” strategy responding to the wider family’s needs, such as supporting children and enhancing parenting and resilience. The role substance use services should play in a system which (Getting our Priorities Right is the title) prioritises child welfare, including what new patients should be asked about the children in their lives. Related local toolkit listed below. For discussion click and scroll down to highlighted heading.
G
‘Toolkit’ to help practitioners safeguard children and families affected by problem substance use (NHS Lothian and partner agencies, 2014). Co-produced by health, social and enforcement authorities in the Edinburgh region. Designed to assist the day-to-day practice of health and social care practitioners working with children and families affected by alcohol and drug problems in the family, but can also act as a checklist and guidance for their managers. Getting it Right in the toolkit’s title echoes the Scottish national guidance listed above. For related discussion click and scroll down to highlighted heading.
G
Key capabilities for treatment staff to work with male perpetrators of domestic violence (2015). Published by King’s College, London, and developed on the basis of UK research (2016). Helps substance use treatment services define and clarify key staff capabilities for working with male substance users who are violent to intimate partners. See also generic NICE quality standards ([UK] National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2016) for health and social care services on assessing and responding to domestic abuse.
G
Good practice in responding to domestic and sexual violence involving substance use (2013). UK guidelines based on a government-funded project intended to improve responses to victims and perpetrators of domestic and sexual violence associated with substance use and/or mental health problems. Includes minimum standards of practice and guidance on policies and procedures. See also generic NICE quality standards ([UK] National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2016) for health and social care services on assessing and responding to domestic abuse.
G
US guidance on substance use treatment and domestic violence ([US] Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 1997). Consensus guidance on how treatment services can identify and work with both perpetrators and victims.
G
Australian guidance on addressing family and domestic violence in addiction treatment ([Australian] National Centre for Education and Training on Addiction, 2013). Among other functions, intended to guide managers in organising policies, procedures and staff training and development to identify and address family or domestic violence among substance use patients.
G
Managing alcohol problems in prisoners (World Health Organization, 2012). Integrated model of best practice in care for problem-drinking prisoners based on UK experience.
G
US consensus guidance on substance use treatment in the criminal justice system ([US] Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2005). Guidance influenced by an impressive array of practitioners and service planners and endorsed by research and practice experts. Distils best research-informed practice on topics including the selection of treatment interventions, matching these to the offender, and planning treatment programmes.
more Retrieve all relevant Effectiveness Bank analyses or search more specifically at the subject search page. See also hot topics on child protection and on helping the families of substance users.
 Close Matrix Bite
Close Matrix Bite 
Links to other documents. Hover over for notes. Click to highlight passage referred to. Unfold extra text 
What is this cell about?
Therapies (cell A5) and therapists (cell B5) matter of course, but so do the management functions of selecting, training and managing staff, and managing the intervention programme. In highly controlled studies, it may be possible to divorce the impact of an intervention from the management of the service delivering it, but in everyday practice, whether interventions get adopted and adequately implemented, and whether staff are able to develop and maintain appropriate attitudes and knowledge, depend on (document listed above) management and supervision.
This cell is about the role played by these management functions in treatment organised and/or funded by criminal justice and other authorities, whose primary aim is to safeguard those in contact with the patient or the wider community. In these contexts, typically treatment is offered or imposed not because it has been sought by the patient, but because it is thought that treating their drinking problems could cut crime, safeguard the drinker’s family, and prevent harm to others through drink-driving or other alcohol-affected behaviour. Even when treatment has been organised primarily to benefit the patient rather than their family or the broader community, these benefits may nevertheless emerge, so this cell may also include studies which document the community and family impacts of treatment in general.
Where should I start?
It is rare to find reviews focused on workforce development in such a narrow sector as substance use treatment in criminal justice contexts, but listed above, the Australian state of Victoria commissioned just such a review to inform its training programme. Published jointly with the Australian government, it benefited from an unusually well resourced national focus on workforce development in substance use treatment. Included in the review was a thoughtful exploration of the role of management, training and supervision in the melding of disparate objectives and philosophies. On the basis of its review of relevant research, the same document also offered guidance to service managers.
Among its messages on training were that: it must focus on offending as well as substance use; along with educational programmes, it can underpin collaboration between criminal justice and treatment systems despite their “very different operating principles, values and procedures”; and managers and supervisors play a key role in making sure skills learnt in training are sustained on return to work.
The justice system usually communicates to the offender that treatment is punishment
Also stressed was that staff competence is critical to implementing rehabilitation in criminal justice settings where “the justice system usually communicates to the offender that treatment is punishment”, and that in turn management is critical to developing and sustaining this competence through training and ongoing support. In cell B5 the we made a similar argument, contending that in criminal justice, child protection and other contexts where treatment is coerced or mandated, staff competence is likely to be even more important than when treatment is given a head start by the client wanting it and wanting to change of their own volition. In turn, this would make management support for staff training and development more important too. Perhaps reflecting this, when a host of possible influences were thrown into the mix, those most strongly related (document listed above) to evidence-based practice in the treatment of offenders in US services included management training, knowledge, and orientation to quality and rehabilitation as opposed to punishment.
The critical role of staff competence in implementing rehabilitation in criminal justice setting was also highlighted by a report on the first trial (document listed above) of training probation officers in the ‘risk-need-responsivity’ model for matching interventions to the offender. It also offered an example of how management can reduce recidivism by organising staff training and ongoing support. More these findings below.
The risk-need-responsivity model
The so-called ‘risk-need-responsivity’ model has been highly influential in guiding treatment interventions with criminal offenders. Its three core principles are:
Risk Providing intensive services to clients at higher risk of reoffending and minimal services to lower risk clients.
Need Target criminogenic needs or the dynamic risk factors which underlie or drive criminal behaviour such as pro-criminal attitudes and substance use.
Responsivity Match the style and mode of intervention to the abilities, motivation, and learning style of the offender.
Highlighted study
Despite the prominence of the ‘risk-need-responsivity’ model in criminal justice treatment interventions ( panel), training offender supervisors to implement this model has rarely been evaluated. Canada hosted the first trial (listed above). From among 80 probation officers a randomly selected 51 were trained using risk-need-responsivity principles to match the intensity of services to an offender’s risk of reoffending, to target the factors which underlie criminal behaviour, and to match intervention style and content to the offender; the remaining 29 officers formed an untrained control group against whom findings from trained officers could be benchmarked. The offenders they supervised were not exclusively problem drinkers or drug users, but generally their substance use seemed a major issue in their offending. Both the model the officers were trained in, and the training itself, stressed targeting problematic attitudes and thoughts using cognitive-behavioural principles, but without formalising these into a manualised programme. This randomised trial showed such training can not only improve officers’ skills and sharpen their practice, but also reduce the recidivism of the offenders
panel), training offender supervisors to implement this model has rarely been evaluated. Canada hosted the first trial (listed above). From among 80 probation officers a randomly selected 51 were trained using risk-need-responsivity principles to match the intensity of services to an offender’s risk of reoffending, to target the factors which underlie criminal behaviour, and to match intervention style and content to the offender; the remaining 29 officers formed an untrained control group against whom findings from trained officers could be benchmarked. The offenders they supervised were not exclusively problem drinkers or drug users, but generally their substance use seemed a major issue in their offending. Both the model the officers were trained in, and the training itself, stressed targeting problematic attitudes and thoughts using cognitive-behavioural principles, but without formalising these into a manualised programme. This randomised trial showed such training can not only improve officers’ skills and sharpen their practice, but also reduce the recidivism of the offenders  chart.
chart.
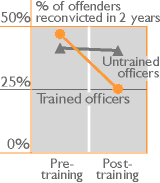
Note from our analysis that the training seems to have embodied effective interactive methods. Perhaps crucially, these included feedback on actual performance and continued post-training support ‘pushed’ to the officers rather than left for them to access (or not) on their own. However, a study of this kind can only make a stab at identifying the active ingredients stimulated by the training which led to the recidivism reductions. Analysis of recordings of supervision sessions suggested that the sole factor which accounted for these reductions was the use of cognitive techniques to alter pro-criminal attitudes – a suggestion difficult to substantiate, as use of these techniques could not be disentangled from the training as a whole and how well the probation officers had taken it on board.
Why this study was so important can be appreciated by turning to cell B5, where we learn that adjustments to the number and frequency of supervision contacts and caseload size (considered proxies for the officer’s ability to exert control over the offender) have generally made no difference to reoffending. Instead, the quality of the work undertaken between supervisor and offender seems the active ingredient. The Canadian study seems to have found a way to improve this quality, and in turn reduce offending. But before you accept the practice implications of its findings, carefully read through our commentary on the study, and ask yourself if you can rely on these findings to guide the training of offender supervisors and how they conduct their supervision, especially unselected supervisors working in the UK context – rather different from these self-selected study participants in Canada. Also ask yourself – as we do in the next section – why the findings were an exception to the generally non-proven record of criminal justice treatment interventions.
Issues to consider and discuss
 Is cognitive-behavioural the way to go?
Published in 2005, our starting point review (discussed above) was upbeat about the interventions available for managers and trainers to build on, declaring that “Recent evaluations … reflect a promising deviation from previous perceptions of ‘nothing works’ to an era of practice that is driven by rigorous program evaluation and evidence-based service delivery”. The reviewers favoured cognitive-behavioural approaches to therapy and the ‘risk-need-responsivity’ model for matching intervention to offender (of which more above), so might have been yet more optimistic had they seen the findings of a later Canadian study listed above and described in the “Highlighted study” section.
Is cognitive-behavioural the way to go?
Published in 2005, our starting point review (discussed above) was upbeat about the interventions available for managers and trainers to build on, declaring that “Recent evaluations … reflect a promising deviation from previous perceptions of ‘nothing works’ to an era of practice that is driven by rigorous program evaluation and evidence-based service delivery”. The reviewers favoured cognitive-behavioural approaches to therapy and the ‘risk-need-responsivity’ model for matching intervention to offender (of which more above), so might have been yet more optimistic had they seen the findings of a later Canadian study listed above and described in the “Highlighted study” section.
That study was concerned with training probation officers to implement supervision based on the risk-need-responsivity model of offender supervision and cognitive-behavioural therapy – an influential family of ‘talking therapies’ which aim to teach new, relapse-preventing ways of acting and thinking.
There seems less cause for optimism when those principles and techniques are packaged into ‘programmes’
Typically the focus is on coping with the triggers, situations or emotional states likely to precipitate relapse. Rather than a set programme, in the Canadian study the training was about principles and techniques.
There seems less cause for optimism when those principles and techniques are packaged into ‘programmes’. Check back on cell A5’s bite which asked, “Why is the record so poor?” – in particular, for cognitive-behavioural programmes. A case in point was the major British study which found that when required by the courts, the main cognitive-behavioural programme (ASRO) applied to problem substance users on probation could not be shown to have reduced reconviction rates relative to sentences without this requirement. The findings were not atypical; no convincing evidence from elsewhere supports such programmes for offenders relative to alternative or usual approaches.
For substance use treatment in general, research findings do not warrant a ‘nothing works’ pessimism about psychosocial approaches, but do suggest that overall ‘nothing works better’ than any other similarly coherent approach. As with other approaches, cognitive-behavioural programmes do not stand out as exceptionally effective. Rather than the specific programme, the key thing may be that training in any convincing new approach instils optimism and re-moralises a perhaps jaded workforce, and offers a coherent treatment rationale via which they can communicate that optimism to the offender – some of the ‘common factors’ highlighted in cell A4’s bite. Training in these approaches also offers trainees specific activities and intermediate targets via which offender and therapist can collaborate, communicate, and develop their relationship – and that has been thought critical since at least Carl Rogers’ seminal work, focused on in cell B4.
What is the essential performance-promoting core of training? Transmission of specific understandings and skills, or are these mainly a vehicle for bolstering non-specific common factors? Can the latter be done without the former? Why the stress on cognitive-behavioural approaches, when these have not yet been proven to be the most effective way to treat substance use problems among offenders? Are cognitive-behavioural techniques active ingredients in generating positive change, and if they are, is it best to try to ensure quality by mandating an expertly crafted programme, or to risk ‘drift’ by focusing on principles and leaving wide discretion to the counsellor or offender supervisor? Might the answer be, ‘It depends’ – on how skilfully the practitioner can use that discretion?
 Is this the most difficult management task in the addictions field?
What we are referring to is running ‘wet’ centres where street drinkers can continue to drink. Here the management challenge seems so daunting that before undertaking it a probing appraisal should be made of whether an organisation’s management, staff and resources, and the way it plans to work with service users, are capable of making things better for clients and community – or could make things worse.
Is this the most difficult management task in the addictions field?
What we are referring to is running ‘wet’ centres where street drinkers can continue to drink. Here the management challenge seems so daunting that before undertaking it a probing appraisal should be made of whether an organisation’s management, staff and resources, and the way it plans to work with service users, are capable of making things better for clients and community – or could make things worse.
Service users in the garden of the Booth wet day centre in Manchester
Two British studies of wet day centres (listed above) and of a residential wet hostel (wet hostel) illustrate the difficult balance between offering a welcoming, relaxed venue which attracts drinkers off the street and avoids them causing offence and concern to local residents and businesses, versus the need to exert some degree of control to ensure safety in the venue, and some degree of therapeutic challenge/pressure to move its clients on to better lives. The risk is that ‘control’ and ‘challenge/pressure’ will generate conflict with the clients and deter attendance, jeopardising the service’s objectives.
Control and therapeutic challenge/pressure risk jeopardising the service’s objectives
Strong, clear management of the right kind was key in both sorts of venues. At the day centres, it was “unusually important that, alongside a strong client oriented ethos, line management functions are vigilantly applied … Persuading and enabling clients to make positive changes is far more difficult than being welcoming and reassuring.” Partly due to management failures, at first the hostel “never developed into a safe environment … and failed to provide services which might further improve [residents’] health and help tackle their alcohol problems … Unwillingness to turn people away … or to enforce a disciplinary code on ‘alcoholics’ considered unable to control themselves contributed to … tension, arguments and sometimes violence which led some residents to leave and deterred potential applicants.” But as at the day centres, difficult as they were, these challenges could be managed: “Management changes helped create a much improved atmosphere: casual ‘drop in’ stayers … were banned, the disciplinary code enforced, and key working properly instituted.” So these projects can operate safely to the benefit of both their users and the local population, but this is by no means a given. Whether they degenerate into just another drinking venue, or make the hoped-for differences to users and the community, are substantially down to management.
 How can you prioritise the child when your patient is the parent?
Cell B5 argued that of all the ‘tricky’ situations treatment practitioners face, “Perhaps trickiest of all is therapy of parents whose substance use and other behaviours might seriously threaten their children’s welfare.” The temptation is to sideline this uncomfortable but crucial work, placing the onus on service managers to counter this through training, support, monitoring and supervision. To managers devolves the task of putting into day-to-day practice the insistence in guidance that child welfare is paramount, despite the fact that their service’s client/patient is not the child, but their parent. Getting our Priorities Right was how the title of Scottish guidance (listed above) formulated the task, and that means envisioning and organising the service as one prong of a multi-agency approach focused not on the parent-patient, but on the family. According to the guidance, it starts (p. 25) with incorporating family-focused questions in the assessment of new patients and continues with an alertness to how changes in their substance use and treatment (such as being detoxified) might affect associated children.
How can you prioritise the child when your patient is the parent?
Cell B5 argued that of all the ‘tricky’ situations treatment practitioners face, “Perhaps trickiest of all is therapy of parents whose substance use and other behaviours might seriously threaten their children’s welfare.” The temptation is to sideline this uncomfortable but crucial work, placing the onus on service managers to counter this through training, support, monitoring and supervision. To managers devolves the task of putting into day-to-day practice the insistence in guidance that child welfare is paramount, despite the fact that their service’s client/patient is not the child, but their parent. Getting our Priorities Right was how the title of Scottish guidance (listed above) formulated the task, and that means envisioning and organising the service as one prong of a multi-agency approach focused not on the parent-patient, but on the family. According to the guidance, it starts (p. 25) with incorporating family-focused questions in the assessment of new patients and continues with an alertness to how changes in their substance use and treatment (such as being detoxified) might affect associated children.
So alien was this to the substance use services of the time, that in 2003 in their Hidden Harm report (listed above), the UK government’s drug policy advisory committee envisaged (p. 82) only a modest direct role for drug and alcohol services, not just now, but in the “medium to longer term”. Even that, they foresaw, “will not be easy [and] will have major resource, staffing and training implications”. How far Britain had to go had been revealed by a survey of drug agencies (an unknown but probably appreciable number of which will also have treated problem drinking) which found “only a handful” made deliberate attempts to assess and meet the needs of their clients’ children. Three years later the advisory committee’s update report (listed above) discerned improvements, but in respect of joint working around substance-using parents or their children, only for around 45% of the services which responded to a further survey.
Why it is so difficult to truly forefront children’s needs – and the risky gaps that can open up without energetic management – was explored by a study in Finland, whose findings will resonate with many in the UK. “Dedication solely to helping the substance abuser” led to a myopia about their children in the beliefs and practices of clinical staff. Insufficiently countered by organisational policies and management, the natural tendency to focus on the face-to-face client meant few questions were asked about children, and then sometimes only as background information on the focal client.
After reviewing relevant research from across the world, UK-based experts on the family dimensions of substance use problems questioned (review listed above) the commonly reported perceptions of treatment workers that addressing child welfare is beyond their skills and professional comfort zones. Though acknowledging differences, the experts’ view was that whether focusing on the patient being treated for substance use problems or on their children, “the same basic skills of forming a therapeutic relationship and counselling” are required.
Substance use problems do not have to be overcome in order to help the child
Reading this review will take you a long way towards appreciating what those skills are, and what supplemental skills and knowledge are needed to better protect children. Once you have read it, take the stance of a manager with substance use-related targets and expectations, and staff who joined the service to tackle dependence on or misuse of alcohol or drugs. A central message of the review is that substance use problems do not have to be overcome in order to help the child. Instead the focus should be on family disharmony and domestic abuse, parental conflict, separation and loss, and inconsistent, neglectful or ambivalent parenting: “The key points here are that as practitioners we can intervene to help these children; and that the focus does not have to be on the parental substance misuse problem, but on promoting necessary beneficial factors in children’s lives.” How far can you go down this road: would it detract from substance-focused work, or would your service risk condemnation and perhaps even closure if you failed to protect children? What would the review’s perspectives mean for staff recruitment and training? Were the UK government’s drug policy advisers right (and are they still) when in 2003 they warned in a report listed above that taking on board child protection “will not be easy [and] will have major resource, staffing and training implications”?
 Close Matrix Bite
Close Matrix Bite 








 Open Matrix Bite guide to this cell
Open Matrix Bite guide to this cell 
 Close Matrix Bite
Close Matrix Bite 

